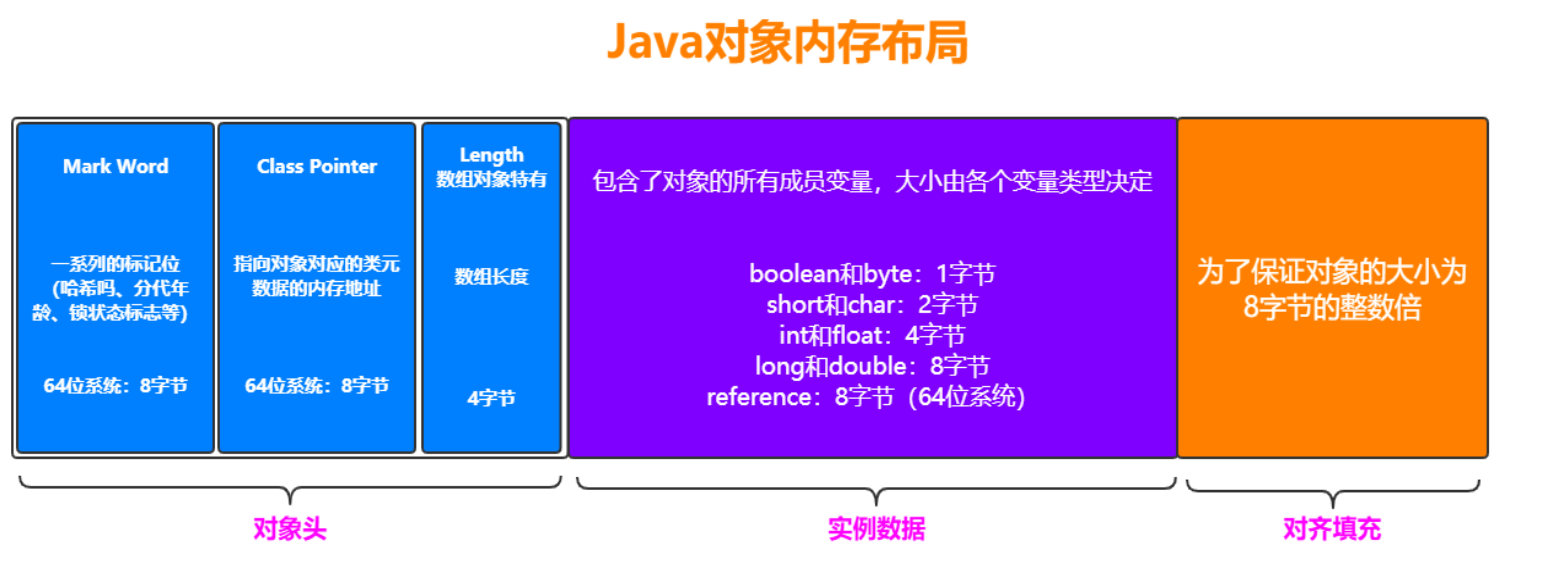
栈帧:每个栈帧对应一个被调用的方法,可以理解为一个方法的运行空间。
每个栈帧中包括
- 局部变量表(Local Variables)
- 操作数栈(Operand Stack)、
- 指向运行时常量池的引用(A reference to the run-time constant pool)、
- 方法返回地址(Return Address)和附加信息。
class Person{
private String name="hua";
private int age;
private final double salary=100;
private static String address;
private final static String hobby="Programming";
public void say(){
System.out.println("person say..."); }
public static int calc(int op1,int op2){
op1=3;
int result=op1+op2;
return result;
}
public static void order(){
}
public static void main(String[] args){
calc(1,2);
order();
}
}//将int类型常量3压入[操作数栈]
//将int类型值存入[局部变量0]
//从[局部变量0]中装载int类型值入栈
//从[局部变量1]中装载int类型值入栈
//将栈顶元素弹出栈,执行int类型的加法,结果入栈
0: iconst_3
1: istore_0
2: iload_0
3: iload_1
4: iadd
【For example, the iadd instruction (§iadd) adds two int values together. It
requires that the int values to be added be the top two values of the operand stack, pushed there by previous instructions. Both of the int values are popped from the operand stack. They are added, and their sum is pushed back onto the operand stack. Subcomputations may be nested on the operand stack, resulting in values that can be used by the encompassing computation.】
5: istore_2
6: iload_2
7: ireturn
//将栈顶int类型值保存到[局部变量2]中
//从[局部变量2]中装载int类型值入栈
//从方法中返回int类型的数据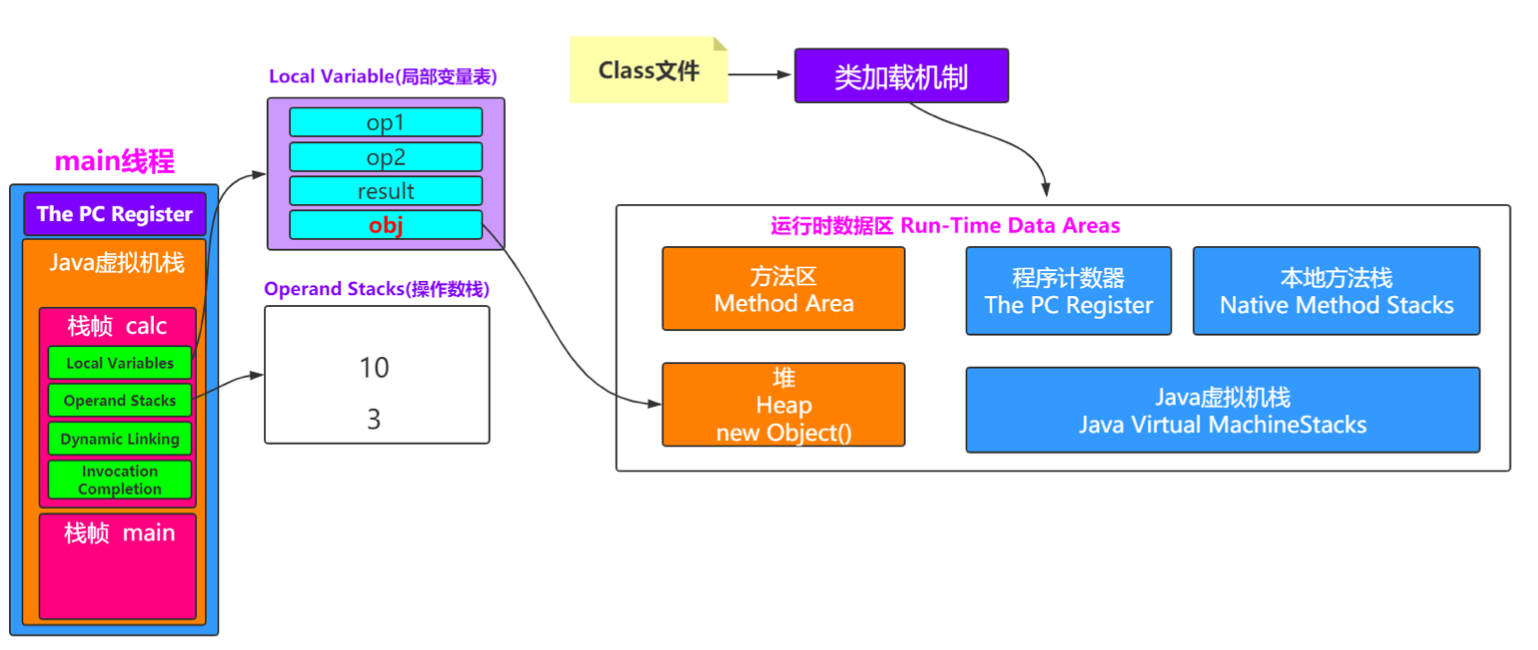
如果在栈帧中有一个变量,类型为引用类型,比如Object obj=new Object(),这时候就是典型的栈中元素指向堆中的 对象。
方法区指向堆:
方法区中会存放静态变量,常量等数据。如果是下面这种情况,就是典型的方法区中元素指向堆中的对象。
private static Object obj=new Object();思考 :一个对象怎么知道它是由哪个类创建出来的?怎么记录?这就需要了解一个Java对象的具体信息咯。
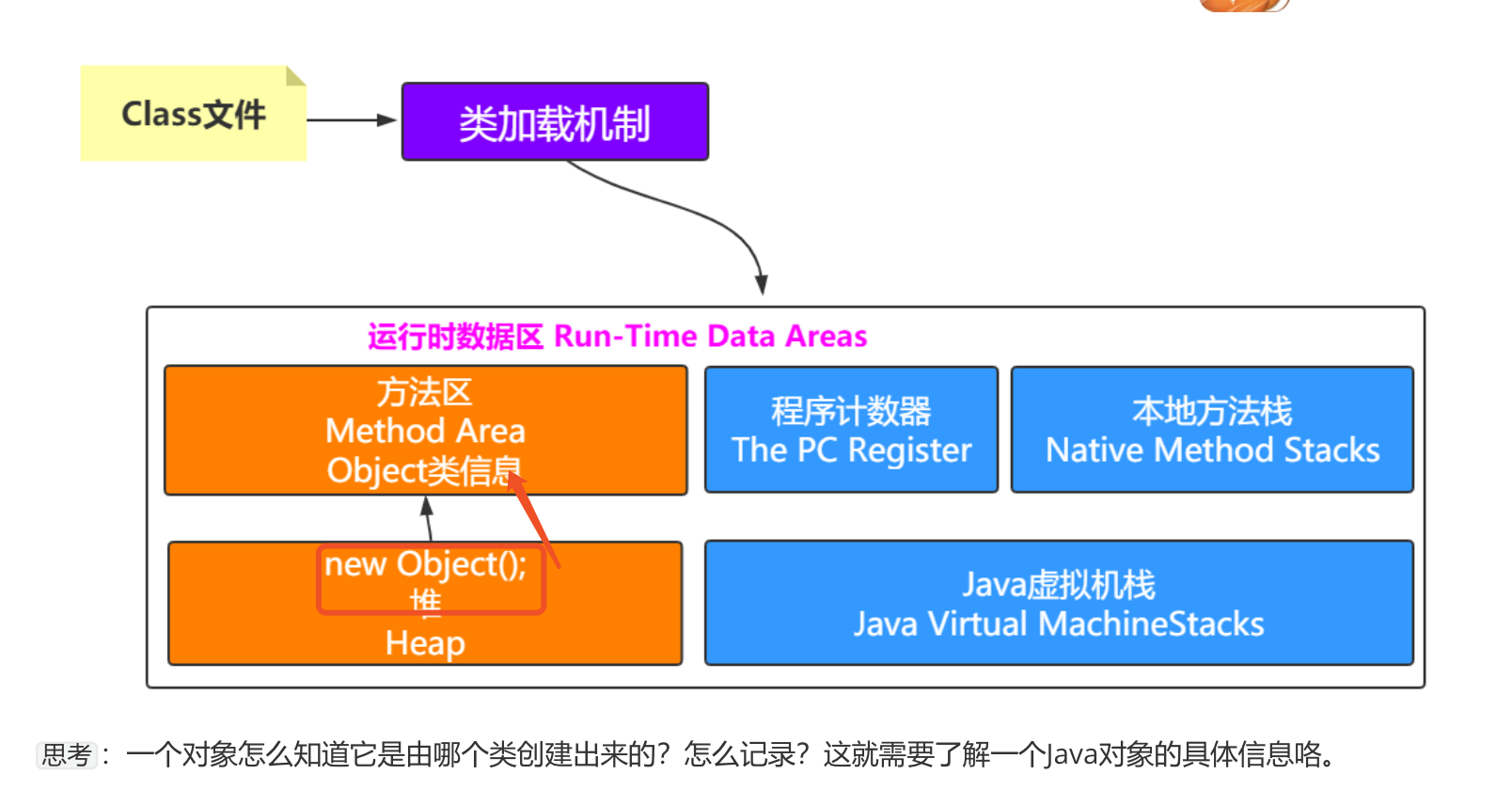
Java对象内存布局
一个Java对象在内存中包括3个部分:对象头、实例数据和对齐填充