IOC源码分析
IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:所谓控制反转,就是把原先我们代码里面需要实现的对象创 建、依赖的代码,反转给容器来帮忙实现。那么必然的我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让 容器知道需要创建的对象与对象的关系。这个描述最具体表现就是我们所看到的配置文件。
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入:就是指对象是被动接受依赖类而不是自己主动去找,换句话说就 是指对象不是从容器中查找它依赖的类,而是在容器实例化对象的时候主动将它依赖的类注入给它。
BeanFactory
Spring Bean 的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的 Bean 工厂,也即 IOC 容器为开发者管理对象 间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在 Spring 中有许多的 IOC 容器的实现供用户选择和使用, 其相互关系如下: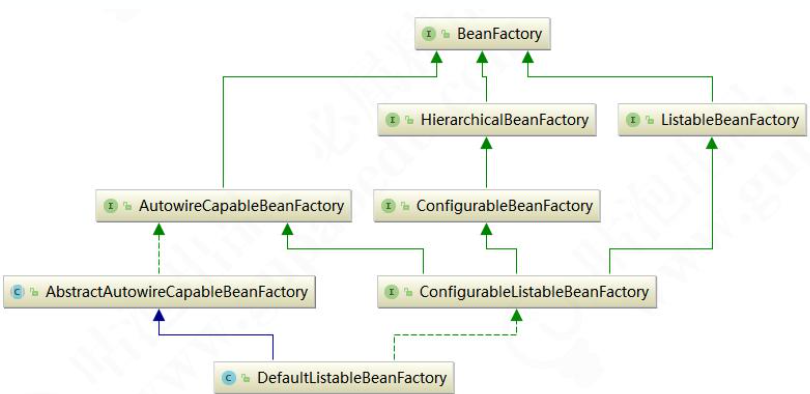
BeanFactory 作为最顶层的一个接口类,它定义了 IOC 容器的基本功能规范,BeanFactory 有三 个重要的子类:ListableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory 和 AutowireCapableBeanFactory。 但是从类图中我们可以发现最终的默认实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory,它实现了所有的接口。
每个接口都有它使用的场合,它 主要是为了区分在 Spring 内部在操作过程中对象的传递和转化过程时,对对象的数据访问所做的限制。 例如 ListableBeanFactory 接口表示这些 Bean 是可列表化的,而 HierarchicalBeanFactory 表示的是 这些 Bean 是有继承关系的,也就是每个 Bean 有可能有父 Bean。AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接 口定义 Bean 的自动装配规则。
ApplicationContext 是 Spring 提供的一个高级的 IOC 容器,它除了能够提供 IOC 容器的基本功能 外,还为用户提供了以下的附加服务。从 ApplicationContext 接口的实现,我们看出其特点:
- 支持信息源,可以实现国际化。(实现 MessageSource 接口)
- 访问资源。(实现 ResourcePatternResolver 接口,后面章节会讲到)
- 支持应用事件。(实现 ApplicationEventPublisher 接口)
基于 Xml 的 IOC 容器的初始化
ApplicationContext 系列容器也许是我们最熟悉的,因为 Web 项目中使用的 XmlWebApplicationContext 就属于这个继承体系,还有 ClasspathXmlApplicationContext 等
IOC运行方法调用时序图:
继承关系图:
1. 寻找入口
还有一个我们用的比较多的 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,通过 main()方法启动:
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");还有像 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 、 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 、 XmlWebApplicationContext 等都继承自父容器 AbstractApplicationContext 主要用到了装饰器模式 和策略模式,最终都是调用 refresh()方法。
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
//设置配置文件路径,
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
//refresh作用是防止IOC容器多次实例化
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}2. 获得配置路径
父类AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext中设置文件路径,
configLocations是一个全局的私有变量,依靠:getConfigLocations来使子类可以获取到
configLocations的值。
@Nullable
protected String[] getConfigLocations() {
return (this.configLocations != null ? this.configLocations : getDefaultConfigLocations());
}
public void setConfigLocation(String location) {
setConfigLocations(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(location, CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}3. 开始启动(整体讲解各个方法作用)
设置完文件的配置路径之后。真正启动是第一步的refresh()方法。
refresh():在AbstractApplicationContext类中。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//1、调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//2、告诉子类启动 refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean 定义资源文件的载入从 //子类的 refreshBeanFactory()方法启动
//创建了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory,当然还进行了资源的载入。在这个内部有loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);方法,目的就是寻找xml文件,进行xml解析,最后一只调用到了XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的doLoadDocument来获取一个完整的xml文档,也就是我们的spring的xml配置文件
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//3、为 BeanFactory 配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等,实际上就是为ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory对象进行属性设定值。BeanFactory是个容器,所以是配置当前容器所应该有的属性。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//4、为容器的某些子类指定特殊的 BeanPost 事件处理器,因为有些属性是不同的BeanFactory容器特有的,对于这写特有的BeanFactory进行处理,默认是AbstractApplicationContext,所以里面没有进行任何的操作行为
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//5、调用所有注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 Bean,内部方法:PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());的属性beanFactoryPostProcessors是在第4步进行初始化的,如果没有的话,只是一个空数组。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//6、为 BeanFactory 注册 BeanPost 事件处理器.
//BeanPostProcessor 是 Bean 后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//7、初始化信息源,和国际化相关.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//8、初始化容器事件传播器.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//9、调用子类的某些特殊 Bean 初始化方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//10、为事件传播器注册事件监听器.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}4. 创建容器
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法调用子类容器的 refreshBeanFactory()方法,启动容器载入 Bean 配置 信息的过程
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//这里使用了委派设计模式,父类定义了抽象的 refreshBeanFactory()方法,具体实现调用子类容器的 refreshBeanFactory()方法
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
AbstractApplicationContext 类中只抽象定义了 refreshBeanFactory()方法,容器真正调用的是 其子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现的refreshBeanFactory()方法,方法的源 码如下:
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果已经有容器,销毁容器中的 bean,关闭容器
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建 IOC 容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//对 IOC 容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用载入 Bean 定义的方法,主要这里又使用了一个委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法,具体的实现调用子类容器
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(),
ex);
}
}在这个方法中,先判断 BeanFactory 是否存在,如果存在则先销毁 beans 并关闭 beanFactory,接着
创建 DefaultListableBeanFactory,并调用 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)装载 bean 定义。
5.载入配置路径
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 中只定义了抽象的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法,容器真正调 用的是其子类 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 对该方法的实现,AbstractXmlApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext { ...
//实现父类抽象的载入 Bean 定义方法
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException
{
//创建 XmlBeanDefinitionReader,即创建 Bean 读取器,并通过回调设置到容器中去,容器使用该读取器读取 Bean 配置资源 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//为 Bean 读取器设置 Spring 资源加载器,AbstractXmlApplicationContext 的
//祖先父类 AbstractApplicationContext 继承 DefaultResourceLoader,因此,容器本身也是一个资源加载器 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
//为 Bean 读取器设置 SAX xml 解析器
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
//当 Bean 读取器读取 Bean 定义的 Xml 资源文件时,启用 Xml 的校验机制 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//Bean 读取器真正实现加载的方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) { reader.setValidating(this.validating);
}
//Xml Bean 读取器加载 Bean 配置资源
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
//获取 Bean 配置资源的定位
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) {
//Xml Bean 读取器调用其父类 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 读取定位的 Bean 配置资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
// 如果子类中获取的 Bean 配置资源定位为空,则获取 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext // 构造方法中 setConfigLocations 方法设置的资源
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
//Xml Bean 读取器调用其父类 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 读取定位 //的 Bean 配置资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
//这里又使用了一个委托模式,调用子类的获取 Bean 配置资源定位的方法 //该方法在 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中进行实现,对于我们 //举例分析源码的 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 没有使用该方法 @Nullable
protected Resource[] getConfigResources() {
return null;
}
}以 XmlBean 读取器的其中一种策略 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 为例。XmlBeanDefinitionReader 调 用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的 reader.loadBeanDefinitions()方法读取Bean配置资源。 由于我们使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 作为例子分析,因此 getConfigResources 的返回值 为 null,因此程序执行 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations)分支。
6. 分配路径处理策略
在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的抽象父类 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中定义了载入过程。
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions()方法源码如下:
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return count;
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource location.
* <p>The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the
* ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver.
* @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader
* @param actualResources a Set to be filled with the actual Resource objects
* that have been resolved during the loading process. May be {@code null}
* to indicate that the caller is not interested in those Resource objects.
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #getResourceLoader()
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[])
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL. //将指定位置的 Bean 配置信息解析为 Spring IOC 容器封装的资源 //加载单个指定位置的 Bean 配置信息
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource…resources) 方 法实际上是调用 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions()方法。
从对 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions()方法源码分析可以看出该方法就做了 两件事:
首先,调用资源加载器的获取资源方法 resourceLoader.getResource(location),获取到要加载的资源。 其次,真正执行加载功能是其子类 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions()方法。在 loadBeanDefinitions()方法中调用了 AbstractApplicationContext 的 getResources()方法,跟进去之 后发现 getResources()方法其实定义在 ResourcePatternResolver 中,此时,我们有必要来看一下 ResourcePatternResolver 的全类图:
从上面可以看到 ResourceLoader 与 ApplicationContext 的继承关系,可以看出其实际调用的是 DefaultResourceLoader 中 的 getSource() 方 法 定 位 Resource , 因 为 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 本身就是 DefaultResourceLoader 的实现类,所以此时又回到了 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中来。
7. 解析配置文件路径
XmlBeanDefinitionReader 通 过 调 用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的 父 类
DefaultResourceLoader 的 getResource()方法获取要加载的资源
DefaultResourceLoader 提供了 getResourceByPath()方法的实现,就是为了处理既不是 classpath 标识,又不是 URL 标识的 Resource 定位这种情况。
在 ClassPathResource 中完成了对整个路径的解析。这样,就可以从类路径上对 IOC 配置文件进行加 载,当然我们可以按照这个逻辑从任何地方加载,在 Spring 中我们看到它提供的各种资源抽象,比如 ClassPathResource、URLResource、FileSystemResource 等来供我们使用。上面我们看到的是定位Resource 的一个过程,而这只是加载过程的一部分。例如 FileSystemXmlApplication 容器就重写了getResourceByPath方法。
通过子类的覆盖,巧妙地完成了将类路径变为文件路径的转换。
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1); }
//这里使用文件系统资源对象来定义 bean 文件
return new FileSystemResource(path); }8.开始读取配置内容
在XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource …)方法看到代表 bean 文件 的资源定义以后的载入过程。
载入 Bean 配置信息的最后一步是将 Bean 配置信息转换为 Document 对象,该过程由
documentLoader()方法实现。
9. 准备文档对象
DocumentLoader 将 Bean 配置资源转换成 Document 对象的源码如下:
/**
* Load the {@link Document} at the supplied {@link InputSource} using the standard JAXP-configured
* XML parser.
*/
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
//创建文件解析器工厂
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
//创建文档解析器
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
//解析 Spring 的 Bean 配置资源
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
/**
* Create the {@link DocumentBuilderFactory} instance.
* @param validationMode the type of validation: {@link XmlValidationModeDetector#VALIDATION_DTD DTD}
* or {@link XmlValidationModeDetector#VALIDATION_XSD XSD})
* @param namespaceAware whether the returned factory is to provide support for XML namespaces
* @return the JAXP DocumentBuilderFactory
* @throws ParserConfigurationException if we failed to build a proper DocumentBuilderFactory
*/
protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory(int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware)
throws ParserConfigurationException {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware);
if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) {
factory.setValidating(true);
if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) {
// Enforce namespace aware for XSD...
factory.setNamespaceAware(true);
try {
factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
ParserConfigurationException pcex = new ParserConfigurationException(
"Unable to validate using XSD: Your JAXP provider [" + factory +
"] does not support XML Schema. Are you running on Java 1.4 with Apache Crimson? " +
"Upgrade to Apache Xerces (or Java 1.5) for full XSD support.");
pcex.initCause(ex);
throw pcex;
}
}
}
return factory;
}10. 分配解析策略
XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类中的 doLoadBeanDefinition()方法是从特定 XML 文件中实际载入 Bean 配置资源的方法,该方法在载入 Bean 配置资源之后将其转换为 Document 对象,接下来调用 registerBeanDefinitions() 启 动 Spring IOC 容 器 对 Bean 定 义 的 解 析 过 程 , registerBeanDefinitions()方法源码如下:
//按照 Spring 的 Bean 语义要求将 Bean 配置资源解析并转换为容器内部数据结构
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//得到 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 来对 xml 格式的 BeanDefinition 解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//获得容器中注册的 Bean 数量
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//解析过程入口,这里使用了委派模式,BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 只是个接口,
//具体的解析实现过程有实现类 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 完成
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//统计解析的 Bean 数量
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
11.将配置载入内存
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 接 口 通 过 registerBeanDefinitions() 方 法 调 用 其 实 现 类 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 对 Document 对象进行解析,解析的代码如下:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
//获得 XML 描述符
this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
//获得 Document 的根元素
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for Environment.acceptsProfiles(String...)
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//在解析 Bean 定义之前,进行自定义的解析,增强解析过程的可扩展性
preProcessXml(root);
//从 Document 的根元素开始进行 Bean 定义的 Document 对象,这里也是第16步,注册bean的起始方法!!!!!!!
//这里也是第16步,注册bean的起始方法!!!!!!!
//这里也是第16步,注册bean的起始方法!!!!!!!
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
//在解析 Bean 定义之后,进行自定义的解析,增加解析过程的可扩展性
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
//创建 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,用于完成真正的解析过程
protected BeanDefinitionParserDelegate createDelegate(
XmlReaderContext readerContext, Element root, @Nullable BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parentDelegate) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(readerContext);
delegate.initDefaults(root, parentDelegate);
return delegate;
}
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}通过上述 Spring IOC 容器对载入的 Bean 定义 Document 解析可以看出,我们使用 Spring 时,在 Spring 配置文件中可以使用
对于既不是
12.载入元素
Bean 配置信息中的
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) {
return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null);
}
/**
* Parses the supplied {@code <bean>} element. May return {@code null}
* if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}.
*/
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
13. 载入元素
和Bean类似,方法名为:parsePropertyElements();
14. 载入的子元素
和Bean类似,方法为:public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String defaultValueType)
15. 载入的子元素
和Bean类似,方法为:public List
16. 分配注册策略
让我们继续跟踪程序的执行顺序,接下来我们来分析 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 对
Bean 定义转换的 Document 对象解析的流程中,在其 parseDefaultElement()方法中完成对
Document 对象的解析后得到封装 BeanDefinition 的 BeanDefinitionHold 对象,然后调用
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils 的 registerBeanDefinition() 方 法 向 IOC 容 器 注 册 解 析 的 Bean , BeanDefinitionReaderUtils 的注册的源码如下:
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
当调用 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils 向 IOC 容器注册解析的 BeanDefinition 时,真正完成注册功能的
是 DefaultListableBeanFactory。
17. 向容器注册
DefaultListableBeanFactory 中使用一个 HashMap:beanDefinitionMap 的集合对象存放 IOC 容器中注册解析的 BeanDefinition,向 IOC 容器注册的主要源码如下:
beanDefinitionMap
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}至此,Bean 配置信息中配置的 Bean 被解析过后,已经注册到 IOC 容器中,被容器管理起来,真正完 成了 IOC 容器初始化所做的全部工作。现在 IOC 容器中已经建立了整个 Bean 的配置信息,这些 BeanDefinition 信息已经可以使用,并且可以被检索,IOC 容器的作用就是对这些注册的 Bean 定义信 息进行处理和维护。这些的注册的 Bean 定义信息是 IOC 容器控制反转的基础,正是有了这些注册的数 据,容器才可以进行依赖注入。



